SpringBoot入门 - 对Hello world进行MVC分层
约 777 字大约 3 分钟
SpringBoot入门 - 对Hello world进行MVC分层
上文中我们创建一个简单的Hello Wold级别的web应用程序,但是存在一个问题,我们将所有代码都放在一个类中的, 这显然是不合理的,那么一个经典的CRUD项目如何分包呢?本文结合常见的MVC分层思路带你学习常见的包结构划分。@pdai
经典的MVC三层架构
三层架构(3-tier application) 通常意义上的三层架构就是将整个业务应用划分为:表现层(UI)、业务逻辑层(BLL)、数据访问层(DAL)。区分层次的目的即为了“高内聚,低耦合”的思想。 1、表现层(UI):通俗讲就是展现给用户的界面,即用户在使用一个系统的时候他的所见所得。 2、业务逻辑层(BLL):针对具体问题的操作,也可以说是对数据层的操作,对数据业务逻辑处理。 3、数据访问层(DAL):该层所做事务直接操作数据库,针对数据的增添、删除、修改、更新、查找等。

用Package解耦三层结构
我们这里设计一个常见的用户增删查改项目,通常来说对应的包结构如下

controller
表示层
package tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.entity.User;
import tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.service.UserService;
/** * @author pdai */
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/** * http://localhost:8080/user/add . * * @param user user param * @return user */
@RequestMapping("add")
public User add(User user) {
userService.addUser(user);
return user;
}
/** * http://localhost:8080/user/list . * * @return user list */
@GetMapping("list")
public List<User> list() {
return userService.list();
}
}
service
业务逻辑层
package tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.dao.UserRepository;
import tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.entity.User;
import tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.service.UserService;
/** * user service impl. * * @author pdai */
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
/** * user dao. */
@Autowired
private UserRepository userDao;
/** * @param user user */
@Override
public void addUser(User user) {
userDao.save(user);
}
/** * @return user list */
@Override
public List<User> list() {
return userDao.findAll();
}
}
dao
数据访问层,数据放在内存中。
package tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.entity.User;
/** * @author pdai */
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
private List<User> userDemoList = new ArrayList<>();
public void save(User user) {
userDemoList.add(user);
}
public List<User> findAll() {
return userDemoList;
}
}
entity
model实体层
package tech.pdai.springboot.helloworld.entity;
/** * User entity. * * @author pdai */
public class User {
/** * user id */
private int userId;
/** * username. */
private String userName;
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
}
运行测试
添加用户
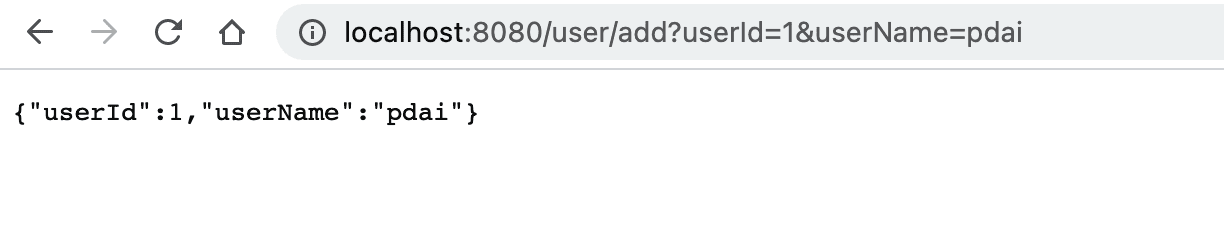 查询用户列表
查询用户列表

示例源码
https://github.com/realpdai/tech-pdai-spring-demos